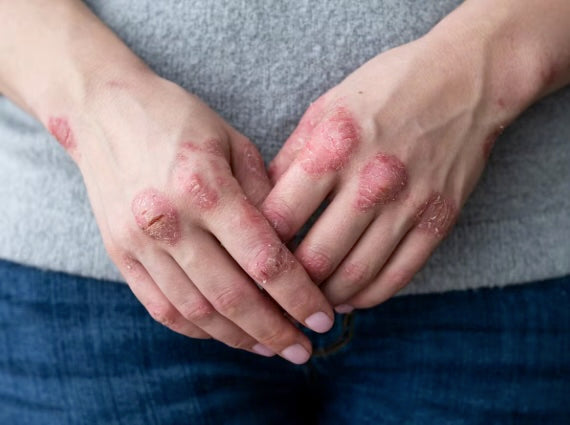
Psoriasis , an autoimmune skin disease affecting millions worldwide, presents as red, scaly lesions, often on the scalp, that can cause severe discomfort.
This form of psoriasis, due to genetic and environmental causes, is notable for its flare-ups that fluctuate in intensity and frequency. Although incurable, proper management can significantly improve the patient's quality of life.
The disease affects all levels of society regardless of gender or age, although some cases are more likely to develop more severe forms, particularly those with a family history of psoriasis or those with comorbidities such as diabetes or lupus. People with fair skin or those who are overweight are also at risk due to a diminished immune response.
To control psoriatic manifestations and relieve symptoms, treatments range from topical and oral medications to phototherapy and even gentler therapeutic approaches. Understanding the specific form and severity of each case is essential for effective psoriasis management.
What is psoriasis?
Psoriasis is an inflammatory skin disease that affects approximately 2 to 3% of the world's population. It can affect people of all ages and ethnic groups. It is a chronic condition that can be debilitating and disabling for those who suffer from it, but it can be well managed and treated if diagnosed and monitored correctly.
Psoriasis is caused by an abnormal immune response within the body that activates skin cells. This activation causes increased growth and maturation of skin cells, which leads to thickening of the top layer of skin and the formation of plaques, which are characteristic of psoriasis.
What are the symptoms of psoriasis?
Psoriasis symptoms can vary depending on the severity and the area of the body affected, but the most common symptoms include itching, redness, scaling and patches of skin, inflammation, thickening of the skin and nails, scratching, and joint pain. People with psoriasis may also experience fatigue and stress, and their skin may become more sensitive.
What are the risk factors for psoriasis?
Risk factors for psoriasis include family history, a history of stress and anxiety, skin injuries, bacterial and viral infections, medications, hormonal changes, and poor nutrition.
What are the treatments for psoriasis?
There are many treatment options available for psoriasis. Topical and systemic medications, essential oils, skin care, and lifestyle changes can all be used to help control psoriasis symptoms.
Using kerato-reducing cream can help combat the symptoms of psoriasis and prevent its occurrence.
What are the possible side effects of psoriasis treatments?
Possible side effects of psoriasis treatments can include rashes, itching, redness, blisters, burning sensations, skin irritation and dryness, headaches, and nausea. People taking systemic medications for psoriasis may also be at risk for infections and heart and/or kidney disease.
What are the ways to prevent psoriasis?
There is no known way to prevent psoriasis yet. However, there are some things you can do to reduce your risk of developing the disease. These include stress management, good nutrition, regular physical activity, avoiding sun exposure and irritating chemicals, and prompt treatment of bacterial and viral infections.
Can young people be affected by psoriasis?
Psoriasis can affect children and teenagers, although they are less likely than adults to develop the disease. In fact, according to the American Academy of Dermatology, psoriasis affects approximately 1 to 2 percent of children and teenagers. Some forms of psoriasis may be more common in younger people, including plaque psoriasis and pustular psoriasis.
What are the psychological and social effects associated with psoriasis?
The psychological and social effects of psoriasis can be significant and can affect the quality of life of people with the disease. Psoriasis symptoms, particularly skin plaques, can cause significant discomfort and self-consciousness in people with psoriasis. People with psoriasis may also experience marginalization and exclusion from certain social activities, which can lead to low self-esteem and anxiety.
How does psoriasis progress?
Psoriasis is a chronic condition that causes clinical signs that can worsen and improve at different times. The disease can be managed and controlled with medications and lifestyle changes, but it is not completely curable. Clinical signs may be more severe during colder seasons and periods of stress.
What tests and diagnostics are available for psoriasis?
Diagnosis of psoriasis is usually made by examining and discussing symptoms with a doctor, and examining the affected skin. Laboratory tests may be performed to rule out other diseases, and the doctor may also evaluate the affected joints and nails to rule out other diseases.
FAQ: Who is affected by psoriasis?
What are the long-term effects of psoriasis?
Psoriasis can lead to long-term complications, including loss of independence, joint pain, and an increased risk of developing certain cardiovascular and autoimmune diseases.
What can people with psoriasis do to manage their condition?
People with psoriasis can take steps to manage their condition, including following appropriate medical treatment, adopting a healthy lifestyle, avoiding risk factors, and listening to their bodies. Additionally, they can rely on psoriasis creams , which will help reduce scales and moisturize the skin.